Compatibility between GPS trackers and Bluetooth sensors, everything you need to know
Reading time
Level

What is a GPS tracker ?
GPS tracking is a technology that uses satellite signals to determine the real-time location of a device or vehicle. Originally developed by the U.S. Department of Defense for military purposes, GPS, which stands for Global Positioning System, has become an integral part of a variety of applications.
A GPS tracker is a specialized device designed to interact with GPS, receiving signals from satellites to precisely determine its location. This compact yet powerful technology facilitates real-time tracking of objects, vehicles or individuals. GPS trackers are available in a variety of forms, from stand-alone units to integrated modules into smartphones or components built into various pieces of equipment.
GPS trackers are not limited to tracking vehicles and equipment; they are also widely used to monitor people’s movements through wearables such as smartwatches, smart safety vests or worker identification badges. Today, GPS tracking systems find applications in fields such as fleet management, asset tracking and personal monitoring.
How does a GPS tracker work?
A GPS tracker works by receiving signals from a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, transmitting data on their precise positions and times of transmission. Using triangulation, the GPS tracker calculates its position by analyzing the travel times of signals from at least three satellites. This information enables the plotter to determine its exact coordinates on the Earth’s surface. Once the calculation is complete, the GPS tracker transmits the acquired location data, providing real-time information on the object, vehicle or individual being tracked, to a central server or user device. The method of data transmission can vary, with some trackers using cellular networks or other communication technologies.
In this article, discover major GPS trackers that integrate seamlessly with our Bluetooth industrial sensors. Our experts take an in-depth look at the functionality and versatility of these trackers, to make tracking simpler and more efficient.
What is the difference between GPS navigation and GPS tracking?
GPS navigation and GPS tracking, although both utilizing Global Positioning Satellites, serve distinct purposes and operate differently. GPS navigation primarily involves the use of apps, built-in systems, or devices to provide directions and location information to users. These systems receive signals directly from GPS satellites, supplemented by Wi-Fi signals and cellular towers for accuracy. GPS navigation focuses on providing real-time guidance, traffic updates, and location-based information to users, aiding in navigation and destination finding.
In contrast, GPS tracking involves the use of devices that receive information from GPS satellites and transmit this data to remote recipients. These tracking devices can be integrated into vehicles or objects, either as hardware components or software applications. They collect location data and send it to designated recipients, enabling remote monitoring of the object’s whereabouts.
GPS tracking is commonly used for fleet management, asset tracking, and surveillance purposes, providing insights into location, speed, behavior, and other pertinent information from a distance. While GPS navigation helps users navigate to specific destinations, GPS tracking facilitates remote monitoring and management of assets and vehicles.
GPS in telematics: a rapidly evolving market
Although the global GPS tracker market is growing, with forecasts suggesting it could exceed $13 billion by 2034 (+/- 13% CAGR between 2025 and 2034), GPS technology alone is no longer enough. Customers expect smart solutions, not just a dot on a map. They want a global view, actionable data, and actionable decisions, but GPS technology has its limitations:
- An inaccurate signal, or even unavailable depending on the environment
- Inaccurate business data, limiting its use
- No event detection (door opening, temperature variation, shocks, etc.)
GPS shows where, but not what is happening. Without context, data does not create value. Today, location alone is not enough: we need to understand. To meet this challenge, hybrid solutions combining the power of GPS with the precision of Bluetooth are becoming increasingly popular every year.
Interoperability of GPS trackers and Bluetooth technology
Some Bluetooth GPS trackers work by combining GPS technology for location tracking with Bluetooth functionality for seamless communication with nearby Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons, sensors, or accessories. These trackers act as Bluetooth gateways, allowing them to detect and communicate with nearby BLE devices.
The trackers use GPS to determine their own location accurately, providing real-time location data. Simultaneously, they scan for nearby BLE accessories or sensors, continuously monitoring their presence. When a BLE device is detected, the tracker collects data from it and transmits it to a designated end platform, such as a cloud-based server or a user’s mobile device.
These Bluetooth GPS trackers come in various forms, including both wired and battery-powered solutions. They can be installed on a wide range of assets, whether mobile or static, to enable comprehensive asset tracking and management. By leveraging both GPS and Bluetooth technologies, these trackers offer enhanced functionality for monitoring assets, improving efficiency, and streamlining management processes.
What are the advantages of hybrid solutions combining GPS trackers and Bluetooth sensors in the field of telematics?
GPS locates, Bluetooth contextualizes. Together, they make telematics smarter. These hybrid IoT solutions enable telematics players to gain operational and economic efficiency.
While GPS trackers play a key role in telematics systems by automating vehicle fleet management, they now also act as routers, transferring data collected by Bluetooth sensors to the customer’s central system (cloud/server) for analysis. In these systems, GPS trackers are usually installed in vehicles and use GPS satellite signals to determine their position. IoT sensors, on the other hand, can be easily installed on equipment. They then communicate using BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) technology with the GPS tracker, which transmits the data in real time to the central server via cellular networks or other communication channels.
Thanks to this technological combination, users will be able to precisely control all their operations and move from reactive to predictive management.
Here is a sample of the uses for which onboard telematics solutions are designed:
Fleet Management
GPS trackers enable fleet managers to monitor vehicle locations and movements in real time, providing valuable information on vehicle usage, fuel consumption, and driver behavior. Integrated with onboard telematics systems, GPS tracker data enables informed decisions to improve fleet efficiency, promote driver safety, reduce operating costs, and improve productivity. In addition, GPS trackers play a key role in effective driver management, enabling route optimization, monitoring of driving habits, and compliance with safety rules.
Reinforced safety
Equipping a fleet of vehicles with an onboard telematics solution also enhances user and equipment safety. Using GPS units and Bluetooth beacons, it is possible to locate vehicles, assets, and operators in real time, protecting them from theft and assault. But it is also possible, through the use of Bluetooth beacons combined with GPS trackers, to ensure, for example, that drivers’ break times are effective or to analyze risky driving behaviors. This comprehensive approach to security enables a rapid response to unauthorized movements or potential security incidents, thereby enhancing the protection of valuable assets in various industrial sectors.
Asset tracking
Asset tracking becomes more effective with the combination of GPS and Bluetooth technologies, which extends beyond vehicles to include logistics and construction equipment, trailers, containers, and other valuable assets. This enables accurate tracking of asset location, usage, and maintenance requirements, facilitating optimized asset lifecycle management.
Predictive maintenance
Implemented in an IoT fleet management solution, GPS trackers can provide insights into vehicle usage patterns, mileage, and engine hours, allowing fleet managers to schedule preventative maintenance and repairs more effectively. By proactively addressing maintenance issues, businesses can minimize downtime, extend asset lifespan, and reduce operational costs.
Reduce operational costs
Acquiring real-time insights into business operations empowers organizations to make informed decisions that can ultimately drive down operating costs. By proactively identifying and addressing issues as they arise, potential cost escalations can be prevented down the line.
One of the key advantages of utilizing GPS trackers is their ability to streamline processes and simplify data collection. With GPS technology, pertinent information is gathered and stored centrally, accessible to all team members who require it. This digitization of operations enhances efficiency and facilitates smoother workflow management.
Improved productivity
GPS trackers enable companies to keep accurate control of the time spent by drivers on the road, on different worksites and on other tasks, promoting greater efficiency and productivity. By leveraging GPS data, companies can optimize routes, ensuring that the nearest vehicle is dispatched to each job site, thus avoiding wasted fuel and time. This strategic approach not only minimizes operational costs, but also optimizes the use of resources, ultimately helping to improve results.
In conclusion, combining the two technologies can offer comprehensive tracking solutions. This combination allows companies to leverage the strengths of each technology based on specific use cases and requirements.
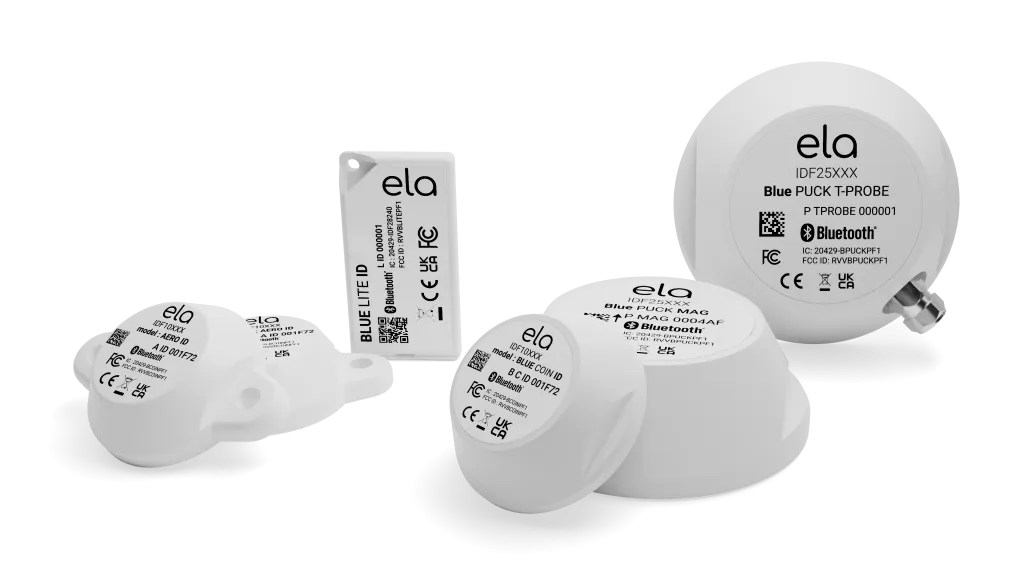

Discover our beacons and Bluetooth sensors compatible with the leading GPS trackers on the market.
Leading GPS Trackers compatible with our Bluetooth sensors
1. Digital Matter
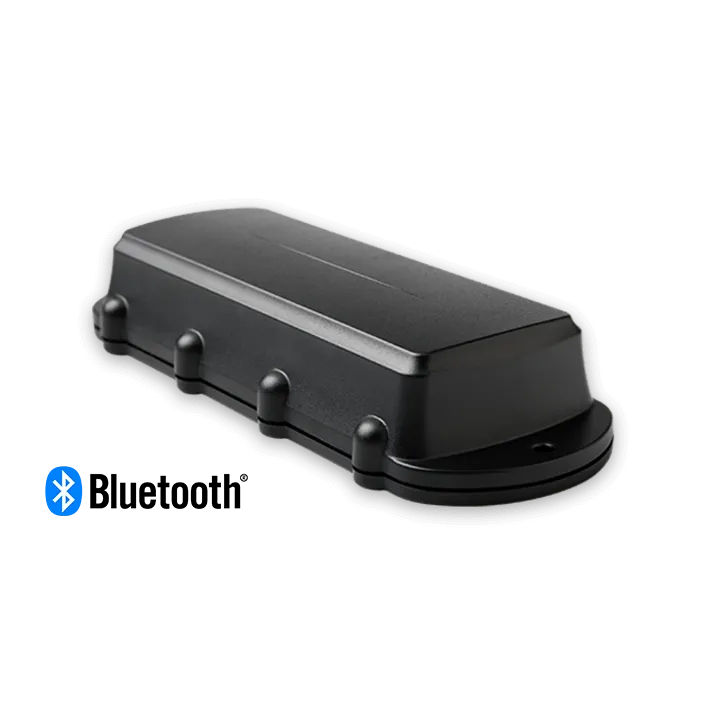

Digital Matter Remora 2, a robust GPS tracking device and Bluetooth gateway, powered by a long-life battery, with tamper detection and 10-year autonomy. Ideal for asset tracking, sensor and tag monitoring, theft recovery, etc. integrates seamlessly with our Bluetooth sensors, enhancing asset tracking and monitoring. Discover the Digital Matter Oyster 3 compatible with our Bluetooth sensors.
2. Geotab
Geotab IOX-BT is designed to monitor Bluetooth proximity tags, including those with public MAC addresses. These beacons, when attached to tools and equipment, play a vital role in optimizing asset utilization, reducing the impact of misplaced equipment, improving productivity, reducing operational costs and ensuring on-time delivery. IOX/BT enhances your asset management by integrating seamlessly with our Bluetooth sensors for precise monitoring. GeotabG09 propels the fleet into the future with increased capacity for extended native vehicle support, better support for fuel economy, electric vehicles and global expansion.

3. ACTIA

ACTIA iCAN is a multi-brand Plug & Play telematics box that connects to the vehicle without assembly to read all the vehicle’s original manufacturer data. It offers the quality and safety guarantees of an “original equipment” automotive supplier. With nearly 15,000 ELA Innovation Bluetooth beacons in service, ACTIA Group’s ICAN is one of the telematics boxes integrating the Blue PUCK, COIN and Blue LITE ranges.
4. ATrack
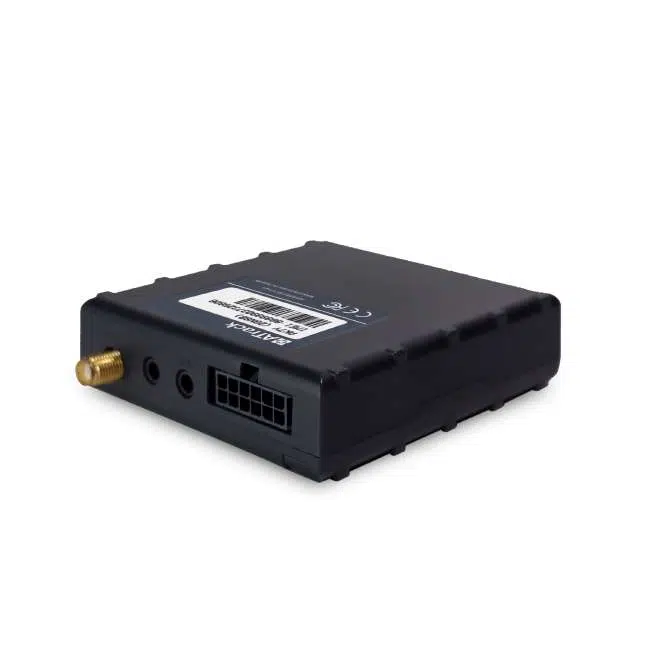

ATrack’s LTE telematics gateway devices can connect to multiple Bluetooth sensors, enabling continuous collection and transfer of sensor data. To ensure top performance, the AK7V telematics gateway collects data on the environment and temperature of refrigerated containers from our Blue PUCK T-PROBE, a Bluetooth temperature sensor that meets the challenges of cold chain traceability.
The integration of the ATrack AS11 with our BLE sensors offers an ideal asset management solution. Enhancing the security of valuable assets and maximizing their efficiency.
5. Teltonika
Teltonika FMB120 is a 2G car tracker offering comprehensive remote monitoring capabilities, making it an ideal choice for rental, taxi, and logistics companies, as well as public transport and personal vehicles.
Our Bluetooth sensors seamlessly integrate with Teltonika FMB920 and FMB001 GPS trackers, enhancing capabilities for driver identification, behavior monitoring, and ensuring driver safety.

6. Ruptela

Ruptela PRO 5 is an advanced GPS tracker designed for different types of vehicle, including trucks, buses and specialized machinery. This tracker offers advanced features, including the ability to read on-board computer (CAN) data, monitor driver actions, manage fuel, and more.
7. Sensolus
Sensolus Track 1100 and 1110 are trackers offering extended battery life thanks to their low power consumption. Both are compatible with our Bluetooth sensors and use NB-IoT connectivity for reliable data retrieval. What’s more, they enable precise, general and area-based localization, meeting a variety of tracking and monitoring needs.
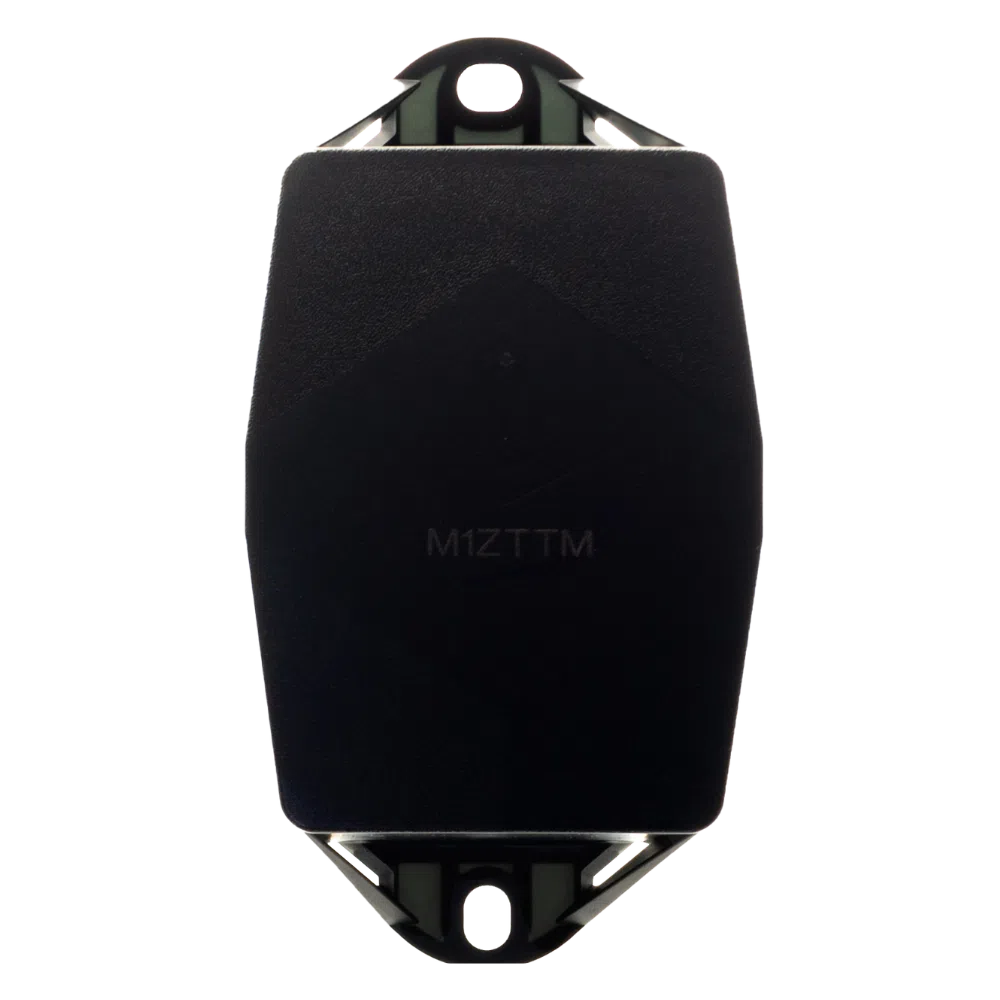

8. Robustel
Robustel’s R2110 High-Speed Smart IoT Gateway delivers advanced wireless connectivity for mobile, smart cities, and industrial applications. With dual cellular modules, it ensures immediate failover to a secondary connection, providing exceptional reliability for IoT applications in dynamic environments and industrial monitoring systems requiring constant uptime.
9. Navtelecom
Navtelecom Smart S-2433, a GPS tracker, features high-quality components to resist voltage fluctuations (up to 350 V). Featuring an optional built-in battery with overload protection, accelerometer, 1-Wire, EcoDriving, automatic firmware updates, Bluetooth and an IP54 enclosure, it offers a robust, full-featured solution.
10. Suntech
Suntech’s ST4955LCBW is a Bluetooth-enabled GPS tracking device utilized across diverse applications. Seamlessly integrates with our Bluetooth sensors. Additionally supports an optional one-wire temperature sensor. Ideal for applications such as trailer or container management and vehicle tracking.
11. Lantronix
Lantronix FOX3 is a compact, all-in-one cellular telematics gateway combining a rich connectivity choice with our powerful Edge intelligence. The cellular FOX3 or SGX5150 preconfigured with a set of BLE beacons capture sensor data such as presence, identification, temperature, humidity and location of goods, people or vehicles.
12. Ercogener
Ercogener’s EG-IOT 1A81 and EG-IOT 1AA6 enclosures are distinguished by their robustness and durability, with IP67/IP69k waterproof certification and shock resistance up to IK09. Equipped with the “EaseEG-IoT” application and supporting a 3FF micro SIM, they offer an integrated solution for demanding telematics and geolocation applications, ensuring monitoring, versatility and precision.
Additionally, our beacons & Bluetooth IoT sensors also offer seamless integration with leading GPS tracker or telematics boxes brands such as the products from Globalstar, Astus, Avema, Cal Amp, Cellocator, Galileosky, Solidrun, TE Connectivity, Telic, Viasat, Xirgo, Quecklink, and many others. This integration enhances connectivity and functionality across various applications, ensuring efficient tracking solutions.