The BLE Gateway is an essential element in the structure of an IoT solution, but do you really know what it is used for? And how does it work?
Whether in our daily lives or in much more industrial fields, Bluetooth wireless communication technology is omnipresent. Indeed, this open protocol is integrated in many devices such as smartphones, tablets or computers, and has greatly contributed to the rapid growth of the connected objects market.
Although Bluetooth technology allows devices to communicate with each other, collecting and sending data back to the cloud or servers is a necessary step.
In this article, we will explain what role the Gateway plays in data management and discuss some concrete examples of use.
What is a BLE Gateway?
A BLE Gateway is a communication portal between Bluetooth devices (e.g. beacons and sensors) and the Cloud/client server, comparable in principle to an internet router. When talking about this element, we sometimes differentiate between the hardware object and the software environment. Being able to communicate via different protocols such as WIFI / Ethernet / Bluetooth or cellular, the Gateway is particularly suitable for industrial applications. Thanks to standard interfaces such as MQTT, API Rest or GRPC, it brings flexibility and efficiency to IoT infrastructures.
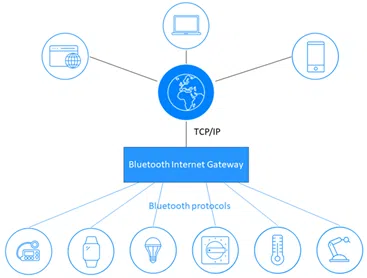
How does a BLE Gateway work?
In order to function and correctly collect data from nearby Bluetooth devices, the BLE Gateway will continuously scan its environment within a range of about 100m. The devices will transmit at regular intervals, to signal their presence to the Gateway. The Gateway will collect their data in the form of frames and publish them on an MQTT broker, so that they can be easily retrieved from the cloud/server.
A Bluetooth Low Energy Gateway can work in Advertising mode, but also in connected mode. The Advertising mode will only allow data collection, while the connected mode will allow sending commands from the cloud/server to the BLE devices via an MQTT broker.

Did you know that?
MQTT stands for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport and is a lightweight messaging protocol particularly suited for sending “small” data between machines. In an MQTT architecture, you will find clients and brokers. The broker is a server that will allow the clients to communicate. The clients can be BLE devices or computers. This messaging protocol is based on the “publish-subscribe” method. The client will subscribe to communication channels called “Topics” on which the devices will publish their data.
Why to use a BLE Gateway?
An IoT solution can work without a Gateway. Nevertheless, it eases the management of a network of BLE devices and simplify data collection.
Indeed, its mission is to collect and route the data sent by the various devices in the vicinity, equipped with Bluetooth. However, a Gateway is not a simple WIFI router. Certain gateways, such as the ELA Innovation BLE Gateway, allow you to go even further than simple data transmission.
Benefits of using a BLE Gateway
Easy to use, industrial gateways are ideal to increase the reliability and efficiency of IoT networks by integrating easily into any infrastructure, whether local or web-based.
In addition to collecting and transmitting data from surrounding connected objects, you will be able to easily configure your network, view and download your data in real time, but also send orders to your devices: such as turning on an LED remotely, triggering an audible alert or in some cases, updating your devices remotely.
Limits of using a BLE Gateway
The main limitations of using a Gateway in your IoT network are the necessity to wire it to power it, as well as to connect it to the Internet. This can represent additional infrastructure costs to be integrated into the overall cost of the solution.
The second point to consider is the appearance of potential breakdowns that could impact the entire network. Indeed, by adding an intermediary between the devices and the cloud, it can create a weak link in the data transmission in case of failure of the Gateway. Yet this problem can be limited by using several gateways in the same network.
Examples of use cases employing an industrial BLE Gateway
IoT is a growing market and more and more companies are integrating it into their digital transformation. If individuals use simple internet routers to access web applications and connect their various devices, companies instead invest in more advanced IoT infrastructures. Let’s discover some use cases.
Smart building and smart office
« Smart Building », a term frequently used to refer to intelligent buildings, is a trend that has exploded in recent years. The development of industrial connected objects has strongly contributed to this trend, since this new building model is based on the collection and analysis of numerous data allowing for better management of energy consumption. To meet this need for information, companies are investing in the latest generation of sensors capable of measuring all kinds of metrics such as temperature, ambient humidity, brightness or even the rate of use of offices and meeting rooms.
To collect and transfer all this data and to access dashboards that show the consumption of a building in real time, network infrastructures rely on IoT infrastructures composed of Bluetooth sensors and gateways, for example.
Tool and parts inventory
Optimizing supply chains is one of the major challenges of Industry 4.0. To facilitate the flow of supplies or to track and inventory tooling fleets in real time, manufacturers are using automatic identification and location systems. By equipping tools and spare parts with identifying tags called beacons, it is possible to track their movements in real time. By using a BLE Gateway, it will allow to record the movements and to upload them on a data visualization platform.
Patient monitoring in the health care
As the number of hospitalizations is constantly growing, hospital performance is a key concern. To improve the patient journey, many hospitals are investing in connected solutions. By using beacons to identify patients, patient records can be easily transmitted from one department to another without losing data. In addition, the use of beacons can also be used to locate patients in hospitals allowing them to find their way around more easily. This will limit delays and no-shows to appointments, saturation of waiting rooms and also crossings and flows of patients. However, in order to guarantee a good experience for patients and hospital staff, it is necessary to rely on an efficient and secure infrastructure. Indeed, as the number of Bluetooth beacons can be very high, it is recommended to use several Gateways in order to facilitate data transmission to the client servers.
Although it is not always necessary to use a gateway to make an IoT infrastructure work properly, it can still be recommended in many cases, such as when the density of Bluetooth devices in a single location is high.