In the constantly evolving world of the Internet of Things (IoT), communication technologies play a crucial role in the development and efficiency of connected solutions. Among these technologies, the Eddystone protocol, developed by Google, is establishing itself as an essential standard for Bluetooth beacons.
In this article, we’ll explore in detail what Eddystone™ is, how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and possible alternatives.
1. Origins and development of the Eddystone™ protocol
The Eddystone™ protocol is an open protocol for transmitting Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) signals developed by Google. Launched in July 2015, it addresses the growing popularity of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons and the interest in proximity technologies.
Before Eddystone, Apple had already introduced the iBeacon format in 2013, which quickly gained popularity. However, iBeacon, while powerful, was a proprietary format, limiting its use to devices and ecosystems compatible with Apple. Google saw an opportunity to create an open and interoperable alternative that could be used on a wider variety of devices.
Designed to enable Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as smartphones, to receive relevant information based on their proximity to Eddystone™ beacons, this protocol is capable of broadcasting short-range data, offering an enriched, contextualized user experience.
Did you know? The name “Eddystone” comes from Eddystone Lighthouse, a famous lighthouse on a reef in England. This choice of name reflects the idea of remote signal broadcasting, similar to the way a lighthouse guides ships, analogous to Eddystone beacons guiding users to relevant, contextual information.
2. Eddystone™ protocol features
a. An open format for greater flexibility
The Eddystone protocol is an open format, accessible to everyone and usable on a variety of devices without proprietary restrictions. This flexibility allows developers and businesses to create customized solutions tailored to their specific needs, thus promoting innovation.
b. Bluetooth frame formats
The Eddystone protocol supports multiple frame types, each designed for specific applications. These frames are broadcasted by Bluetooth beacons and can be used in various ways to interact with surrounding devices.
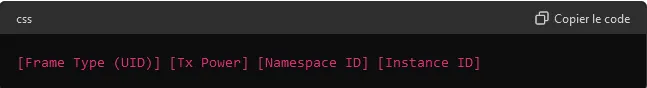
1. Eddystone-UID
The Eddystone-UID format broadcasts a unique identifier, composed of a Namespace ID (10 bytes) and an Instance ID (6 bytes). This identifier is used to uniquely identify a particular beacon within a set of beacons.
Applications :
- Asset tracking: Companies can track the location of important assets in real-time.
- Navigation and geolocation: users can be guided through complex buildings such as shopping malls or airports.
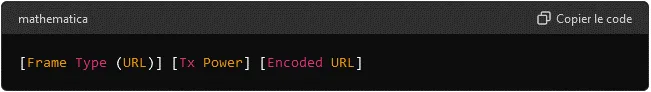
2. Eddystone-URL
Physical Web concept: The Eddystone-URL frame allows for broadcasting a compact and optimized URL to be detected by nearby devices. This feature is the basis of Google’s Physical Web concept, where physical objects can directly interact with users through web links.
Applications :
- Proximity marketing: Stores can send specific offers or promotions to nearby customers.
- Contextual information: In a museum, for example, visitors can receive additional information about an exhibit when approaching a beacon.
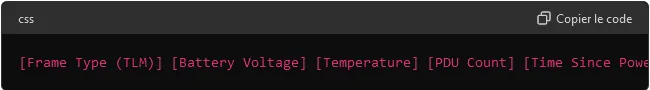
3. Eddystone-TLM (Telemetry)
Environmental data collection: the Eddystone-TLM frame broadcasts telemetry data such as temperature, battery level, reset counter and activation time.
Applications :
- Proactive maintenance: Administrators can monitor beacon status and schedule maintenance before a tag fails.
- Environmental analysis: Temperature data and other metrics can be used to monitor conditions in a warehouse or data center.
4. Eddystone-EID (Ephemeral ID)
Secure applications: The Eddystone-EID format distributes ephemeral identifiers that change periodically. These identifiers are generated to be valid only for a limited time, and can only be interpreted by authorized devices.
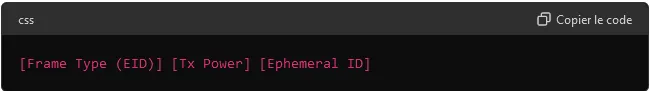
Importance of ephemeral identifiers:
- Security and privacy: Ephemeral identifiers prevent unauthorized tracking and protect user privacy.
- Secure authentication: Used in applications requiring secure authentication, such as mobile payments or secure access to facilities.
3. How the Eddystone protocol works
a. Eddystone beacon
Eddystone beacons are small BLE transmitters programmed to broadcast data packets at regular intervals. Each beacon is configured with a unique identifier and can transmit different types of packets, including unique identifiers (UID), URLs (URL), and telemetry data (TLM).
b. Broadcasting Data Packets
When an Eddystone beacon is activated, it starts broadcasting data packets. These packets are picked up by nearby Bluetooth-compatible devices (gateways, routers, GPS trackers, smartphones, etc.). Each packet contains specific information, such as a unique identifier to identify the beacon, a URL to redirect to an online resource, or telemetry data to monitor the beacon’s status. The broadcast interval can be configured according to needs (e.g., from every 100ms to every few seconds). Eddystone packets are encapsulated in standard BLE packets and broadcasted by the BLE module.
c. User interaction :
When a user with a compatible smartphone enters the range of an Eddystone beacon, their device picks up the data packets broadcasted by the beacon. Depending on the content of these packets, specific actions can be triggered on the user’s device. For example, if the beacon broadcasts a URL, the device can automatically open the web browser and load the associated page. Similarly, if the beacon sends telemetry data, the device can display information such as temperature or battery level.
d. Personalization and Contextualization
One of Eddystone’s major strengths lies in its ability to offer highly personalized and contextual user experiences. By leveraging precise location and the data broadcasted by beacons, developers can create tailored interactions that adapt to users’ specific needs and interests. For example, a museum can use Eddystone beacons to provide information about exhibits as visitors move through the galleries.

Discover our Bluetooth beacons compatible with the Eddystone protocol.
4. Advantages and disadvantages of the Eddystone protocol
Pros:
The Eddystone protocol offers several advantages that distinguish it from other Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacon formats. Here are the main advantages:
1. Open Format
Eddystone is an open format, which means it is accessible to everyone and can be used without proprietary restrictions. This facilitates adoption and integration into a variety of applications and devices.
2. Interoperability
Thanks to its open format, the Eddystone protocol can be used on a wide range of devices and platforms, including Android and iOS systems, without requiring specific hardware or proprietary licenses.
3. Enhanced security
The Eddystone-EID frame offers secure ephemeral identifiers, preventing unauthorized tracking and protecting user privacy. This is essential for applications requiring a high level of security, such as mobile payments and secure access.
4. Battery management
The Eddystone beacons are designed to be energy-efficient. They can operate for months or even years on a single battery, thanks to optimized broadcast cycles and efficient standby modes.
5. Data Collection and Monitoring
The Eddystone-TLM format allows for the collection of telemetry data such as temperature, battery level, and other parameters, facilitating proactive beacon management and predictive maintenance.
6. Compatibility with Google Services
The Eddystone protocol integrates well with various Google services, such as Google Nearby and Google Maps. This enables the creation of enriched user experiences and leverages Google’s geolocation and proximity search features.
7. Scalability
Eddystone beacons can be deployed on a large scale in a variety of environments, such as shopping malls, airports, museums and smart cities. Their flexibility and ability to broadcast different types of frames make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
8. Community Support and Documentation
As an open format, the Eddystone protocol benefits from a large community of developers and contributors. There is extensive documentation and online resources available to assist with the implementation and customization of beacons.
In summary, the main advantages of Eddystone lie in its flexibility, openness, ability to support secure applications, and compatibility with a wide range of devices and services. These characteristics make it an attractive choice for developers and businesses looking to leverage BLE beacon technologies to enhance user interaction and optimize their operations.
Cons:
1. Dependence on Bluetooth:
Despite its compatibility with a wide range of devices, some older or non-BLE-compliant devices may not be able to detect or interpret Eddystone signals correctly. Furthermore, universal adoption is not guaranteed, and some systems may favor other standards such as Apple’s iBeacon.
2. Configuration and Update :
Initial configuration and updates of beacons can be tedious, especially in environments where hundreds or thousands of beacons are deployed. Remote management tools can help, but they also require additional infrastructure and ongoing management.
5. Alternative protocols to Eddystone
Although the Eddystone protocol is a robust solution for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons, other protocols also offer interesting features for specific applications. Let’s look at some of the most popular alternatives:
iBeacon
Developed by Apple, iBeacon was introduced in 2013 and is one of the first BLE protocols to gain widespread adoption. Here are some key features:
Apple ecosystem integration: iBeacon is tightly integrated with the iOS ecosystem, offering seamless compatibility with Apple devices.
Proprietary: Unlike Eddystone, iBeacon is a proprietary format, which means its use is limited to Apple-compatible devices.
How it works: iBeacon uses unique identifiers to transmit signals to nearby iOS devices, triggering specific actions such as opening apps or displaying notifications. To find out more about this protocol, read this article.
Applications :
Proximity marketing: retailers can send targeted promotions to iPhone users entering their stores.
Indoor Navigation: Used in large spaces such as shopping malls and stadiums to assist with navigation.
AltBeacon
Developed by Radius Networks, AltBeacon is an open-source protocol designed to offer a flexible and interoperable alternative to proprietary formats. Here are its key strengths:
Open-Source: As an open format, AltBeacon enables unrestricted adoption and customization, encouraging innovation and experimentation.
Interoperability: Compatible with a wide range of devices and platforms, AltBeacon can be used in a variety of environments without the need for special hardware.
Applications :
Large-scale deployments: Ideal for projects requiring a customizable, cost-effective solution.
Customized solutions: Developers can adapt the protocol to specific needs, such as security or asset management systems.
Physical Web
A Google project, Physical Web aims to make physical objects accessible via simple Bluetooth interaction, without the need for specific applications. Here are its features:
Easy discovery: users can discover and interact with nearby objects by detecting URLs broadcast by beacons.
Simplicity: no dedicated application is required; users can use their web browser to access the information.
Applications :
Contextual Information: Museums can broadcast information about exhibits using Physical Web beacons.
Application-free interaction: Ideal for environments where users may not want to download specific applications.
Protocol comparison
To help you better understand the differences and strengths of each protocol, here is a comparison chart:
| Eddystone | iBeacon | AltBeacon | Physical Web | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Developer | Apple | Radius Network | ||
| Type of protocol | Open | Proprietary protocol | Open | Open |
| Compatibility | Multi-platform | iOS mainly | Multi-platform | Multi-platform |
| Usage | Marketing, navigation, data monitoring | Proximity marketing | Custom solutions | Contextual information |
| Complexity of set-up | Medium | Low | Medium | Low |
| Security | Ephemeral identifiers | Static identifiers | Static identifiers | public URLS |
Choosing the right Bluetooth protocol depends on your specific needs and the environment in which it will be deployed. The Eddystone protocol offers a flexible and secure solution, ideal for a wide range of IoT applications. However, iBeacon, AltBeacon and Physical Web also offer unique advantages that may be better suited to certain situations.
By evaluating the features and benefits of each protocol, you can select the most suitable solution to maximize the efficiency and user interaction of your IoT projects.